Stratifies NAFLD Patients And Diagnoses NASH and NASH cirrhosis

Diagnoses NASH and NASH cirrhosis with LIVERFASt™
LIVERFASt™ is a blood-based test that provides a complete liver assessment and diagnosis for fibrosis, cirrhosis, activity and steatosis from early to late NASH stages.
LIVERFASt™ Identifies NAFLD Among Patients With MetS
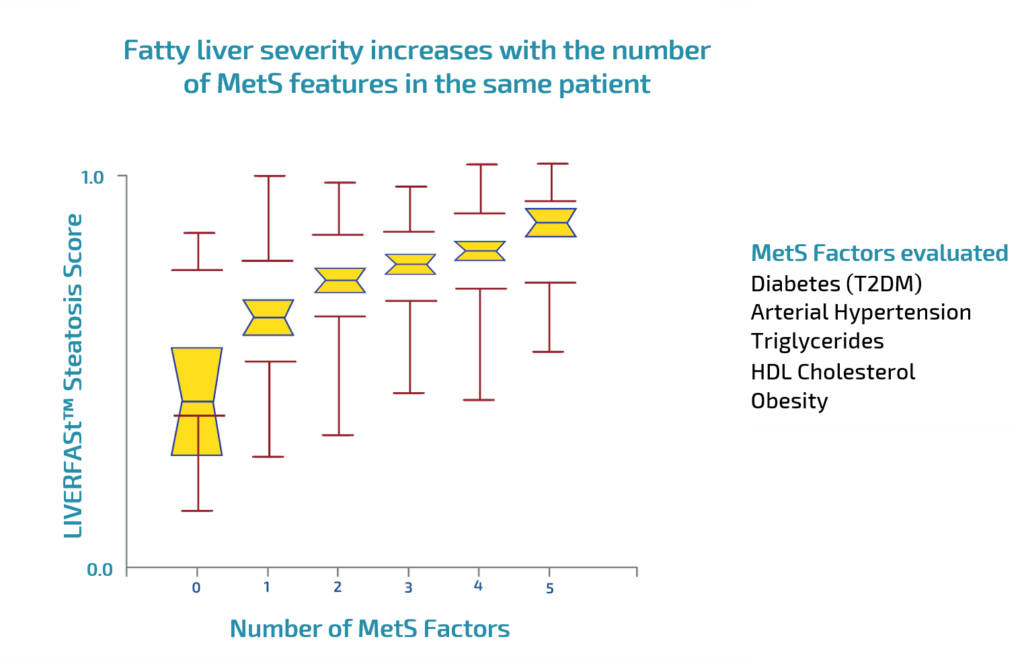
The median scores of LIVERFASt™ tests increase with the number of MetS factors.
LIVERFASt™ stratifies NAFLD according to fibrosis stage and activity and steatosis grades.
LIVERFASt™ performs similarly for patients with obesity and diabetes.
Reliable Results Compared To Elastography
LIVERFASt™ provides reliable results in patients with conditions where liver stiffness measurement by elastography could not:
- Severe obesity (risk of failure of elastography)
- Severe steatosis (risk of overestimation of liver stiffness)
- Significant liver cytolysis upper than 3 times ULN (risk of overestimation of liver stiffness)
LIVERFASt™ Outperforms Other Standards Of Care
LIVERFASt™ provides higher accuracy for cirrhosis in both diabetic and non-diabetic patients:
For severe fibrosis and cirrhosis:
- Performed comparably to elastography with better applicability and no failure
- Outperformed FIB-4 in the identification of cirrhosis and severe fibrosis in Type 2 Diabetes NAFLD patients.
For early fibrosis:
- Better performance than elastography without bias from inflammatory activity and steatosis.
For steatosis:
- Better grading of steatosis than liver ultrasound and controlled attenuation parameter (CAP).
LIVERFASt™ Has Similar Accuracy To Transient Elastography For Cirrhosis Diagnosis But With Better Applicability
References
- Chalassani N, et al. Hepatology. 2018 Jan;67:328-357.
- Younossi ZM, et al. Hepatology. 2016;64:73–84.
- Aravind A, et al. JILSA. 2020;12:31-49.
- De Lédinghen V, et al. Hepatology 2020.72;1:906A
- Raskin M, et al. Hepatology 2020.72;1:273A
- Decraeckeer M. et al., Aliment Ther Pharmacol 2022
- Cohn B, et al. Hepatology 2020.72;1:943A
- De Ledinghen V, et al. J Hepatol 2021:#198 (abstract)
- Ratziu V, et al. 2005 Jun;128:1898-906.
- Diehl AM, et al. NEJM. 2017; 377: 2063-2072.
- Wong RJ, et al. Gastroenterology. 2015;148: 547-55.





