Publications

LIVERFASt (L-FAST) Identifies Advanced (F3F4, AF) and Clinically Significant Fibrosis (F2-F4, CSF) in MASLD Patients
In a biopsy-validated cohort of MASLD patients (n=399, with 235 T2D), combining LIVERFASt with Fibroscan correctly identified 95%

The Utility of Non-Invasive Tests (NITs) – LIVERFASt, FIB4 and VCTE (Fibroscan) in MASH Patients
This publication evaluates the real-world use of non-invasive tests (LIVERFASt, FIB-4, and VCTE) in monitoring MASH patients undergoing

Association between Psoriasis Severity & Steatosis Measured by AI-based Algorithm (LIVERFAStTM)
This publication explores the relationship between psoriasis severity and liver steatosis using the AI-based LIVERFASt tool. Patients with

LIVERFASt (L-FAST) Identifies Advanced (F3F4, AF) and Clinically Significant Fibrosis (F2-F4, CSF) in MASLD Patients
In a biopsy-validated cohort of MASLD patients (n=399, with 235 T2D), combining LIVERFASt with Fibroscan correctly identified 95%

The Utility of Non-Invasive Tests (NITs) – LIVERFASt, FIB4 and VCTE (Fibroscan) in MASH Patients
This publication evaluates the real-world use of non-invasive tests (LIVERFASt, FIB-4, and VCTE) in monitoring MASH patients undergoing

Association between Psoriasis Severity & Steatosis Measured by AI-based Algorithm (LIVERFAStTM)
This publication explores the relationship between psoriasis severity and liver steatosis using the AI-based LIVERFASt tool. Patients with

Retrospective cross sectional evaluation of the LIVERFASt Test for staging liver fibrosis in MASLD patients in NIDDK studies’ populations using liver biopsy
MASLD affects more than 25% of subjects of the general population and can progress to advanced fibrosis
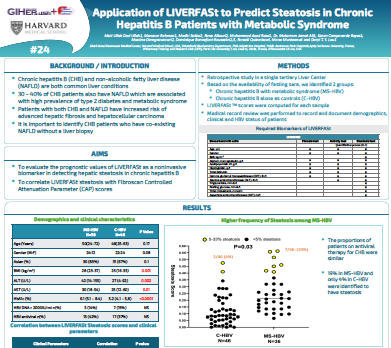
Application of LIVERFASt Biomarkers to Evaluate Longitudinal Hepatic Fibrosis and Inflammation after HCV cure
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is a common cause of both liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Successful Direct

Comparison of the prevalence of advanced fibrosis (AF) using two combinations: Liver stiffness measurement (LSM or VCTE Fibroscan) along with LIVERSTAT (LST) or FIB-4 in a prospective chronic liver diseases (CLD) cohort
AI-based blood tests LIVERSTAT for advanced fibrosis (AF) in patients with T2D can streamline the diagnostic process. Aim



